What is the solution for leachate treatment?
Leachate is wastewater collected from landfills. From the landfill process, under the influence of water naturally contained in the waste and natural (such as rain, storms, morning dew, …) the water passes through the waste layers to the leachate reservoir.
Leachate has a very high concentration of pollutants, so the problem of treating leachate to meet standards is still facing many difficulties not only in Vietnam but also in countries around the world.
The reason leachate has not been thoroughly treated is that to treat it to meet discharge standards, it is necessary to invest in high technology with quite expensive costs, making it difficult to make a profit. On the contrary, if only using conventional solutions, it is impossible to treat leachate to meet discharge standards into the environment.

Leachate contains many pollutants with high concentrations. At landfills, the pollution index value varies according to the composition of the waste and the age of each landfill.
Properties and composition of pollutants at landfills
Table 1: Leachate quality index before treatment:
| Parameter | Unit | New landfill (< 2 -3 years) | Long-term landfill ( > 3 years) | Long-term landfill ( > 10 years) |
| pH | 4.5 – 7.5 | 6.6 – 7.5 | ||
| BOD5 | mg/l | 2.000 – 20.000 | 100 – 200 | |
| COD | mg/l | 3.000 – 60.000 | 100 – 500 | |
| TDS | mg/l | 2.000 – 60.000 | ||
| Total Nitrogen | mg/l | |||
| Amoni Calculated by Nitrogen | mg/l | 10 – 800 | 20 – 40 |

Table 2: Maximum allowable concentrations of pollution parameters in wastewater from solid waste landfills according to QCVN 25:2009 BTNMT are presented in the following table:
| Parameter | Maximum allowable concentration (mg/l) | ||
| A | B1 | B2 | |
| BOD5 (20 oC) | 30 | 100 | 50 |
| COD | 50 | 400 | 300 |
| Total Nitrogen | 15 | 60 | 60 |
| Amoni Calculated by Nitrogen | 5 | 25 | 25 |
In there:
– Column A specifies the maximum allowable concentration when discharged into water sources used for domestic water supply purposes;
– Column B1 specifies the maximum concentration when discharged into water sources not used for domestic water supply purposes (January 1, 2010);
– Column B2 specifies the maximum allowable concentration when discharged into water sources not used for domestic water supply purposes (January 1, 2010).

Understanding the difficulties that the wastewater industry faces, we offer a solution to treat leachate using ROCHEM RO membrane technology combined with chemical and biological methods. Applying high technology but still saving investment and operating costs
ROCHEM RO membrane technology solution for leachate treatment provided by TVTS
ROCHEM’s RO membrane module is specialized in filtering and treating wastewater. The difference between ROCHEM’s RO membrane module and other RO membranes is due to the design of the tube module structure, stacked discs combined with open channels and vortex flow

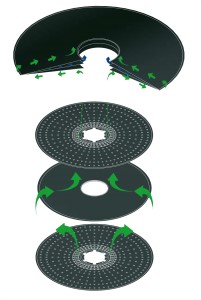
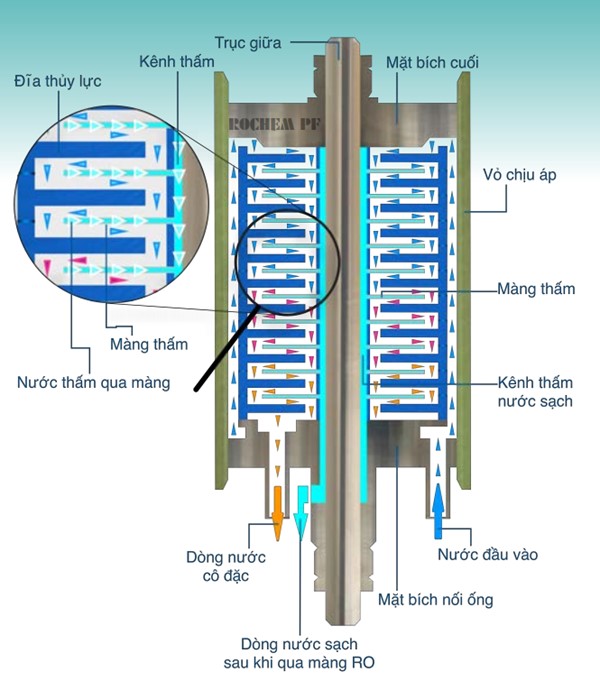
Comparison of processing capacity between ROCHEM RO membrane & other RO membranes:
| Target | Rochem RO membrane module | Other RO membranes |
| Sludge density index of wastewater | SDI = max 20 | SDI < 5 |
| Turbidity of wastewater | NTU = max 5 | NTU = 1 |
| Dissolved solids | TDS = max 42.000 ppm | TDS < 32.000 ppm |

Advantages of ROCHEM RO membrane technology in leachate treatment
– Minimize clogging
– Technology has been proven effective worldwide
– Can handle wastewater containing very high levels of COD, BOD, Nitrogen, Ammonium
– Ensure optimal operating costs, low total operating costs for the entire product life cycle
– Ensure long membrane life
– Total investment and operating costs are lower than traditional treatment systems with the same flow rate



